There are a lot of open forums and discussions due to the Log4j zero-day flaw these days. Log4j is an open-source Java-based library developed by Apache Software Foundation, as it’s used for logging error messages. CVE-2021-44228 announced that there is a remote code execution vulnerability that is being exploited widely and all Java-based applications may be a potential target. Jenkins was one of them on the list :(. Luckily there was a shout from the Jenkins security team that Log4j is not used in the Jenkins core and the only risk is a plugin that uses Log4j.
In this tutorial, I’m going to help you to quickly identify if some of your Jenkins plugins are using Log4j.
Prerequisites
- Jenkins instance
Solution
Step 1. Open your desired browser and type your Jenkins domain with the /script at the end.
https://your-jenkins-domain/script
Step 2. To check if the log4j is included in your Jenkins installed plugins run the following Groovy script in the script console and click the Run button.
org.apache.logging.log4j.core.lookup.JndiLookup.class.protectionDomain.codeSource
Step 3. If you get the same result as on the picture below:
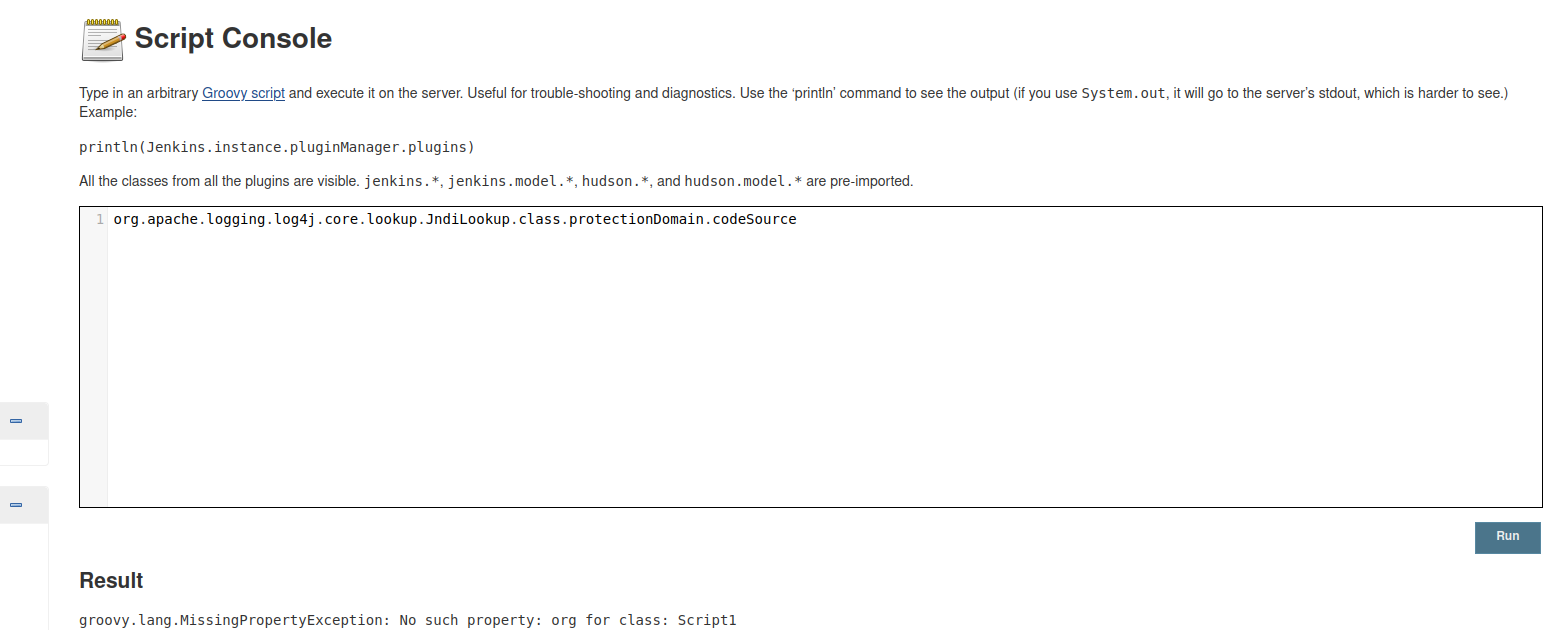
groovy.lang.MissingPropertyException: No such property: org for class: Script1
That means that Log4j is not included in any of your installed plugins and there is no potential security risk. Otherwise, the output from the script console will print the path location where Log4j is found.
Note If you are curious and want to check some Log4j protections methods for your Elasticsearch stack take a look at Protect Elasticsearch stack from Apache Log4j vulnerability.
Conclusion
The only advice to protect your Jenkins instance, if the Log4j is found is to disable the plugin or temporarily remove it until there isn’t any new patched version announced. Feel free to leave a comment below and if you find this tutorial useful, follow our official channel on Telegram.